A
Adapter:
A device that allows you to connect a CCD camera to many scientific instruments or lenses. Also referred to as mount adapter and lens mount adapter. See also C and CS Mounts.
A/D Clock:
internal reference time of the A/D converter.
A/D Converter:
Analog-to-digital converter. In a CCD camera system, the electronic circuitry that converts the analog information (continuous amplitudes) acquired by the detector into the digital data (quantified, discrete steps) used to display the image. See also A/D conversion.
Address:
Tipically as interface bus address. D.T.A. camera (old models) tipically only uses the FDL-PCI interface, which is mounted into a free slot of the PCI bus on your PC. FFFFFFFFH plugging-play mode, the address specification is not necessary.
ADU:
Analog-to-digital unit. A number representing a CCD's output. The relationship between the ADUs generated and the number of electrons acquired on the CCD is defined by the system gain. Also referred to as count and digital number .
Amplifier Delay:
Very old camera parameter to specify the CCD amplifier delay in us.
Analog:
A scheme for representing data via continuous amplitudes current or voltage.
Analog-to-digital converter:
See A/D converter.
Analog-to-digital unit:
See ADU.
A
Adattatore:
Dispositivo che permette di collegare la CCD camera ad una vasta gamma di strumenti scientifici o altri obiettivi. E' anche detto mount adapter e lens mount adapter. Vedi anche Attacchi C e CS
A/D Channel:
Canale di conversione analogico-digitale utilizzato. E’ possibile utilizzare uno o piu' canali di conversione: quando sul ns computer e' riportato il valore 0 riferito a questa voce, viene utilizzato un solo canale di conversione. In caso di piu' canali, essi vengono numerati in ordine crescente conseguenzialmente.
A/D Clock:
base dei tempi del convertitore A/D.
A/D Converter:
Analog-to-digital converter. In un sistema di acquisizione con camera CCD, e' costituito dal circuito che converte il segnale analogico (ampiezze continue) in uscita dal sensore CCD in un dato digitalizzato ( passi discreti ) usati per mostrare l'immagine. Vedi anche A/D conversion
Address:
Normalmente riferito all'indirizzo dell’interfaccia sul bus. La serie di camere DTA utilizzavano tipicamente l’interfaccia FDL-ISA di cui necessitava conoscere l'indirizzo poi si é utilizzato la FDL-PCI, questa veniva montata in uno slot libero del bus PCI del proprio PC. FFFFFFFFH impostato come indirizzo indicava la modalita' plugging-play, per cui non era necessario la specificare alcun indirizzo.
ADU:
Analog-to-digital unit. E' il numero che rappresenta l'output del sensore CCD. La relazione tra ADU generati e numero di elettroni acquisiti dal CCD e' definito dal gain del sistema. E' anche chiamato count e digital number.
Amplifier Delay:
Indicava il ritardo dell’amplificatore in us, parametro che deriva dai primi modelli prodotti.
Analog:
Schema per rappresentare dati attraverso correnti o tensioni continue.
Analog-to-digital converter:
Vedi A/D converter.
Analog-to-digital unit:
Vedi ADU.
B
Bias:
In a CCD camera system, the minimum intensity required for each exposure (equivalent to performing a zero-second exposure with the shutter closed) to obtain positive signal from the CCD sensor. The bias, which is not user selectable, is set at the factory and remains stable over the lifetime of the camera system. See Bias section.
Binning:
In CCD imaging technology, the technique of combining the charge from adjacent pixels so that the total charge can be read out as an image at the expense of spatial resolution. See also the Binning section.
B
Bias:
In un sistema di acquisizione con camera CCD e' la minima intensita' richiesta per ogni esposizione (equivalente a fare una ripresa di zero secondi di esposizione con l'otturatore chiuso) perche' si ottenga un segnale in uscita dal CCD positivo. Il bias, che non e' selezionabile dall'utente, e' fissato dal tipo di costruzione e rimane costante per tutto il funzionamento del sistema CCD camera. Vedi anche la sezione Bias
Binning:
Nell'acquisizione di immagini con sensori CCD, e' la tecnica di unire pixels adiacenti per formarne uno piu' grande a spese della risoluzione spaziale. Vedi anche la sezione Binning.
C
Camera Add:
Intrinsic address of the DTA camera. It is possible connecting more than one DTA device to your PC. First of the series always has address=0, the following ones are numbered in increasing order.
Camera Identifier:
It is an intrinsic datum memorized in the status memory of the platform currently in use and specifies the camera model.
CCD:
Charge-coupled device. A light-sensitive silicon chip used as a photodetector in digital camera systems. CCDs are manufactured in a wide variety of formats, architectures, and grades. See CCD section.
Charge:
In CCD imaging technology, a measure of the number of electrons confined by a pixel.
Contrast:
It shows the contrast percent in the image calculated according to the following equation
![]()
where Imax and Imin are the maximum and minimum intensity values inside the image or the window to which the datum refers
C-mount:
A standard screw-in lens mount common to some scientific instruments. More info.
Cooled CCD:
A charge-coupled device that is operated below ambient temperature in order to reduce or eliminate dark current. CCD cooling is often achieved via Peltier (thermoelectric) coolers or cooled liquid gases.
C
Camera Add:
Indirizzo intrinseco della DTA Camera. E’ possibile collegare al ns PC piu' di un dispositivo DTA. Il primo della serie ha sempre come indirizzo 0, le seguenti sono numerate in ordine crescente conseguenzialmente.
Camera Identifier:
E’ un dato intrinseco memorizzato nella memoria di status della piattaforma in uso e ne specifica il modello.
CCD:
Charge-Coupled Device. E' un chip al silicio sensibile alla luce usato come photodetector nei sistemi con camere digitali. I CCD sono costruiti in vari formati, architetture e gradi. Vedi la sezione CCD
Charge:
Nella tecnologia di acquisizione di immagini con sensori CCD, indica il numero di elettroni prodotti da ogni pixel.
Contrast:
Indica la percentuale di contrasto nella immagine calcolato secondo la seguente equazione
![]()
dove Imax e Imin sono I valori massimo e minimo dell'intensita' all'interno della immagine o della window a cui il dato si riferisce.
C-mount:
E' lo standard di avvitamento degli obiettivi per alcuni strumenti scientifici. Maggiori dettagli.
Cooled CCD:
Un sensore CCD che opera ad una temperatura inferiore alla temperatura ambiente al fine di ridurre il fenomeno della dark current. Il raffreddamento del sensore CCD e' spesso ottenuto usando un Peltier (termoelettrico) o gas liquidi a basse temperature.
D
Dark current:
The charge accumulated in a pixel, in the absence of light. See also dark current.
Dynamic range:
The ratio of the maximum (brightest) to minimum (darkest) signal levels present in an image. For instance, a true 12-bit digital camera is capable of providing a dynamic range of 4096:1. See A/D.
D
Dark current:
E' la carica accumulata generata da un pixel in assenza di luce. Vedi anche la sezione dark current.
Dynamic range:
E' il rapporto tra il livello massimo (piu' chiaro) e quello minimo (piu' scuro) del segnale presente in una immagine. Per esempio, una camera digitale a 12-bit e' capace di fornire una dinamica di 4096:1. Vedi A/D.
E
Electromagnetic Spectrum (EM): (From Wikipedia)
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The "electromagnetic spectrum" of an object has a different meaning, and is instead the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object.
See EM
E
Electromagnetic Spectrum (EM): (From Wikipedia)
Lo spettro elettromagnetico (abbreviato spettro EM), in fisica, indica l'insieme di tutte le possibili frequenze delle radiazioni elettromagnetiche.
See EM
Exposure time:
The length of time for which the user wants to expose the CCD sensor to the ligth.
Exposure time:
La lunghezza di tempo per cui si vuole esporre il sensore CCD alla luce.
F
Filter wheel:
It shows the presence of the filter wheel, specifying the model in use, if there is one.
Frame:
The image area.
Frame buffer:
In a digital imaging system, the hardware in which the frame memory (RAM that stores full frames of the image signal) resides.
Full well capacity:
The number of electrons that can be held in one pixel. It is assumed that all pixels on a CCD have the same full well capacity.
Fw port type:
Filter wheel port used for its control.
Fw port address:
Filter wheel port address, if one exist.
Front/back illuminated CCD:
It shows the lighting mode of the CCD sensor in use.
F
Filter wheel:
Indica la presenza della ruota portafiltri, specificando, in caso affermativo, il modello in uso.
Frame:
Quadro che costituisce l'immagine.
Frame Buffer:
In un sistema di cattura delle immagini digitale, e' l'hardware nel quale risiede la memoria del frame dell' immagine. (RAM che raccoglie il full frame del segnale dell' immagine).
Full well capacity:
Il numero massimo di elettroni che puo' essere contenuto in un pixel. In un sensore CCD si assume che tutti i pixel abbiano la stessa full well capacity.
Fw port type:
Tipo di porta che interfaccia la ruota porta filtri in uso.
Fw port address:
Indirizzo della porta che controlla la ruota porta filtri.
Front/back illuminated CCD:
Indica la modalita' di illuminazione del sensore CCD in uso.
G
Gain:
A/D conversion gain in e/ADU (e for electrons and ADU for Analogical Digital Unit)
Gray level:
The brightness of a pixel in an image, expressed as an integer. Gray levels range from
0 (black) to 255 (white) for an 8-bit digital signal
0 (black) to 4095 (white) for a 12-bit digital signal.
0 (black) to 65535 (white) for a 16-bit digital signal.
Also referred to as gray value. See ADU.
G
Gain:
guadagno del convertitore A/D, in e/ADU (e sono elettroni mentre ADU sta per Analogical/Digital Unit)
Gray level:
Indica la luminosita' di un pixel in una immagine, espressa come un intero. I livelli di grigio vanno da
0 (nero) a 255 (bianco) per un segnale digitale ad 8-bit.
0 (nero) a 4095 (bianco) per un segnale digitale ad 12-bit.
0 (nero) a 65535 (bianco) per un segnale digitale a 16-bit.
Anche chiamato valore di grigio. Vedi anche ADU
H
Hot Pixel:
It is a more more luminous pixel than the other pixels in the image and his aspect is like a small point very brilliant. It can be deleted by subtracting the Dark Frame or by software.
H
Hot Pixel (pixel caldo):
E' un pixel piu' luminoso degli altri nell'immagine e ha l'aspetto di un puntino molto brillante. Viene eliminato sottraendo il Dark Frame o in alcuni casi via software.
I
Infrared [IR]:
The region beyond the visible spectrum at the red end, it has wavelengths between about 750 nm and 1 mm.
See Electromagnetic Spectrum.
I
Infrared [IR]:
La regione adiacente al campo di luce visibile subito dopo il rosso, con lunghezze d'onda comprese tra circa 750nm e 1mm.
Vedi Spettro Elettromagnetico.
K
Kurtosis:
It is a pure number, that measures as much as a distribution is flat or claimed, with respect to the normal distribution.

where x1,x2,...xn are the pixel values into the the current window,
the mean value of them,
the standard deviation,
N number of pixels inside the window, the -3 constant allows to obtain zero for athe Normal distribution.
If Kurt > 0, the distribution is called leptokurtic and it is more claimed than the normale distribution.
If Kurt < 0, the distribution is called platykurtic and it is flat.
K
Kurtosis:
Per come e' definito, e' un numero puro, che misura quanto una distribuzione sia piatta o piccata, rispetto alla distribuzione normale.

Dove x1,x2,...xn sono i valori dei pixel all'interno della window attiva,
e' il loro valor medio,
e' la standard daviation,
N e' il numero di pixel della window, la costante -3 viene introdotta solo per ottenere zero nel caso di una distribuzione normale.
Se Kurt > 0 , la distribuzione e' chiamata leptokurtic ed e' piu' piccata della distribuzione normale.
Se Kurt < 0, la distribuzione e' chiamata platykurtic ed e' piatta.
L
Light:
A form of electromagnetic radiation. Visible light (400 nm to 770 nm) can be perceived by the unaided human eye. See infrared and ultraviolet.
Linearity:
In CCD imaging technology, precise linearity dictates that image bright is exactly proportional to the subject bright.
Link Type:
Type of link from PC to DTA camera. The types of links commonly available are parallel, coaxial, by optic fibre.
L
Luce:
Una forma di radiazione elettromagnetica. La luce visibile (da 400 nm a 700 nm) puo' essere percepita dall'occhio umano. Vedi anche infrarosso e ultravioletto.
Linearita':
Nella tecnologia di imaging, per linearita' si intende che la immagine ha una luminosita' direttamente proporzionale a quella del soggetto.
Link Type:
Tipo di collegamento da PC a DTA camera. I tipi di collegamenti comunemente disponibili sono parallelo, coassiale, a fibra ottica.
M
Maximum Value:
It shows the maximum value among all the pixels inside the active window.
Media of Area:
It shows the mean value among the pixels of the current region of interest.
Minimum Value:
It shows the maximum value among all the pixels inside the active window..
Mpp CCD:
Multi-pinned-phase operation. A mode that reduces the rate of dark current generation by a factor of 20 or more.. Also called inverted operation.
M
Maximum Value:
Indica il valore massimo contenuto nei pixels della window attiva sulla immagine.
Media of Area:
Indica il valor medio tra i valori dei pixels contenuti nella window attiva sulla immagine corrente.
Minimum Value:
Indica il valore minimo contenuto nei pixels della window attiva sulla immagine.
Mpp CCD:
Multi-Pinned Phase operation. Un modo di ridurre la velocita' della generazione di dark current di un fattore 20 o piu'. Chiamata anche Inverted operation.
N
Noise:
An unwanted or undesirable signal. See system noise.
Number of gain:
Number of default gain available with which the device can be used.
N
Noise:
Un segnale non desiderato. Vedi anche rumore del sistema
Number of gain:
Numero di guadagni presettati con cui il dispositivo puo' essere utilizzato.
O
Output amplifier:
A mechanism in the CCD that amplifies the electrons in the output node sufficiently to get the signal to the A/D converter. The output amplifier is the primary source of read noise.
Output node:
The location on a CCD where charge is collected as a discrete picture element for CCD readout. Data enters the output node from the serial register and exits to the A/D converter.
O
Output amplifier:
Il meccanismo all'interno di un CCD che amplifica gli elettroni nel nodo di uscita per rendere il segnale sufficientemente alto da essere letto dal convertitore A/D. L'amplificatore e' la sorgente primaria del rumore di lettura.
Output node:
Nel CCD il luogo in cui viene raccolta la carica come un elemento discreto del CCD readout. I dati entrano nell'output node dai registri seriali e escono verso il convertitore A/D.
P
Platform:
DTA Camera model.
Pixel:
(picture element) it s the smallest piece of information in an image.
Port type:
Type of port used to connect PC and DTA camera.
PTF FILE:
The current DTA camera senttings are seved on a .cfg file. This field shows the file path name . The name of file is automatically chosen by Vista in according to the Camera model and CCD sensor.
P
Platform:
Modello della camera DTA in uso.
Pixel:
(picture element) è il più piccolo elemento che fornisce informazioni sull'immagine
Port type:
Porta di collegamento tra PC e DTA Camera.
PTF FILE:
I settaggi correnti della DTA camera in uso, vengono salvati su un file .cfg. Questo campo indica l’indirizzo del file e il nome dello stesso. Il nome si riferisce al modello della piattaforma e del sensore CCD.
Q
QE:
Quantum efficiency. The measure of the capacity of an imager to produce electronic charge from incident photons. Especially important to perform low-light-level imaging. See also the section Quantum Efficiency
Q
QE:
Efficienza quantica. La capacita' di un dispositivo di imaging di trasformare i fotoni incidenti in elettroni.Particolarmente importante per imaging a bassi livelli di luce. Vedi anche la sezione Efficienza Quantica.
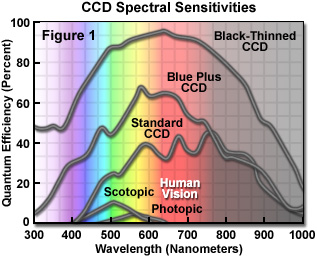
R
Read noise:
In CCD imaging technology, unwanted signal or disturbance that is generated by the on-chip output amplifier. Also called preamplifier noise. See also the noise section.
Region of interest:
A user-defined, rectangular area (a square is common) on a CCD or on a image that is exposed and processed as an image. See also window section.
Resolution:
A measure of how fine a detail can be detected, in terms of either space (spatial resolution), time (temporal resolution), or intensity.
R
Read noise:
Nella tecnologia CCD, un segnale indesiderato che generalmente e' prodotto dall' alimentatore di uscita on-chip. E' chiamato anche preamplifier noise. Vedi anche la sezione rumore
Region of interest:
E' un'area rettangolare o quadrata definita dall'utente su un sensore CCD o su una immagine, che sara' quindi esposta e processata come una immagine. Vedi anche la sezione window.
Resolution:
La misura del piu' piccolo dettaglio rilevato, in termini di spazio (risoluzione spaziale) , di tempo ( risoluzione temporale) o di intensita'.
S
Sampling Freq.:
Sampling frequency (us or MHz).
Shutter:
Shutter model used.
Shutter dly:
It shows the shutter intrinsic delay. In fact, one of the shutter features is its mechanical delay that is not removeable.
Skewness:
It is a pure number, with which to measure the asymmetry of a distribution with respect to his mean value.
where x1,x2,...xn are the pixels values inside the current window,
is the average of them,
is the standard daviation, N the number of pixels inside the current region of interest.
If Skew > 0 the distribution is unbalanced to right of the mean value.
If Skew < 0 the distribution is unbalanced to left of the mean value.
If Skew =0 the distribution is perfectly symmetric with respect to the average. (ideal case)
Spatial resolution:
Standard deviation:
It shows the std among the pixels into the current region of interest or image.
Status:
The status registers are not modifiable registers of the present memory inside the DTA camera. They contain inside the intrinsic device information (for instance the number which identifies the model, code of the sensor CCD, information about the presence of the filter-wheel).
Sum of Area:
sum of the pixels values inside the selected window
S
Sampling Freq. :
Frequenza di campionamento (us o MHz)
Shutter :
Modello dell’otturatore in uso.
Shutter dly:
Questo dato riporta il ritardo intrinseco dell’otturatore in uso. Esso e' caratterizzato da un ritardo nella chiusura, ineliminabile dal punto di vista meccanico.
Skewness:
Per come e' definito, e' un numero puro, con cui misurare l'asimmetricita' di una distribuzione rispetto al suo valor medio.

Dove x1,x2,...xn sono i valori dei pixel all'interno della window attiva,
e' il loro valor medio,
e' la standard deviation, N e' il numero di pixel della window.
Se Skew > 0. la distribuzione e' sbilanciata a destra del valor medio.
Se Skew > 0 , la distribuzione e' sbilanciata a sinistra del valor medio.
Se Skew =0 ( caso puramente ideale), e' perfettamenete simmetrica rispetto alla media.
Spatial resolution:
Vedi risoluzione
Standard deviation:
Indica la std tra i pixels contenuti nella window attiva della immagine corrente.
Status:
I registri di Status sono registri non modificabili della memoria presente all'interno della DTA camera. Essi contengono all'interno delle informazioni intrinseche del dispositivo (per esempio il numero che ne identifica il modello, codice del sensore CCD, informazioni sulla presenza della ruota portafiltri)
Sum of Area:
Somma tra loro i valori contenuti dai pixels all'interno della window selezionata
T
Temporal resolution:
Refers to the precision of a measurement with respect to time.
Time Base:
For the coordination of the times of working of the device, it is necessary for it to have inside a time of reference with which measure it, every time one executes an operation.
T
Temporal resolution:
Si riferisce alla precisione di una misura rispetto al tempo.
Time Base:
Per la coordinazione dei tempi di funzionamento del dispositivo, e' necessario che esso abbia al suo interno un tempo di riferimento con il quale misurarsi,ogni volta che esegue una una operazione. Questo dato fornisce dunque la base dei tempi correntemente usata dalla piattaforma.
U
Ultraviolet [UV]:
The region of the spectrum from about 400 nm (just beyond the violet in the visible spectrum) to about 40 angstroms (on the border of the x-ray region).
See Electromagnetic Spectrum.
U
Ultravioletto [UV]:
La regione dello spettro compreso tra 400nm ( giusto al di sopra della regione del visibile, dopo il viola) e i 40 angstrom circa ( al di sotto della zona dei raggi-X).
Vedi Spettro Elettromagnetico.
V
Values Range:
It shows the values-range of the pixels of the active window. Range=maximum value - minimum value
Variance:
It shows the variance among the pixels of the active window.
In probability theory and statistics, variance measures how far a set of numbers is spread out. A variance of zero indicates that all the values are identical. Variance is always non-negative: a small variance indicates that the data points tend to be very close to the mean (expected value) and hence to each other, while a high variance indicates that the data points are very spread out around the mean and from each other.
V
Values Range:
Indica il range di valori contenuti nei pixels della window attiva sulla immagine. Values Range=maximum value-minimum value.
Variance:
Indica la varianza tra i pixels contenuti nella window attiva della immagine corrente.
La varianza e' il valor medio del quadrato degli scarti, cioe' la la somma dei quadrati degli scarti per le relative probabilita'.
Una varianza di zero indica che tutti i valori sono identici.
La varianza è sempre positiva: una piccola varianza indica che i punti dati tendono ad essere molto vicino alla media (valore atteso) e, quindi, tra loro, mentre una elevata varianza indica che i punti dati sono molto sparsi intorno alla media e l'uno dall'altro.
W
Window Area:
It shows the window area in pixels
Window Dimension:
Width and height of the active window on the image in pixels.
Window start:
It shows the coordinates of beginning point of the active window on the image (top angle on the left) in pixels.
W
Window Area:
Area della window attiva sulla immagine in pixels.
Window Dimension:
Larghezza e altezza della window attiva sulla immagine in pixels.
Window start:
Indica le coordinate del punto di inizio della window attiva sull'immagine (angolo in alto a sinistra) in pixels.

